Disovery of a Dynamically Cold Disc Galaxy at z=7.31
Published in MNRAS
In this work, we present high-resolution ALMA observations of REBELS-25, which we identify as the most distant confirmed rotating disc galaxy observed to date. This discovery challenges the prevailing expectation that early galaxies, formed in the aftermath of the Big Bang, would be irregular and turbulent, shaped by frequent mergers and rapid accretion. Instead, REBELS-25 exhibits a well-ordered, thin rotating disc, similar to nearby spiral galaxies like the Milky Way.
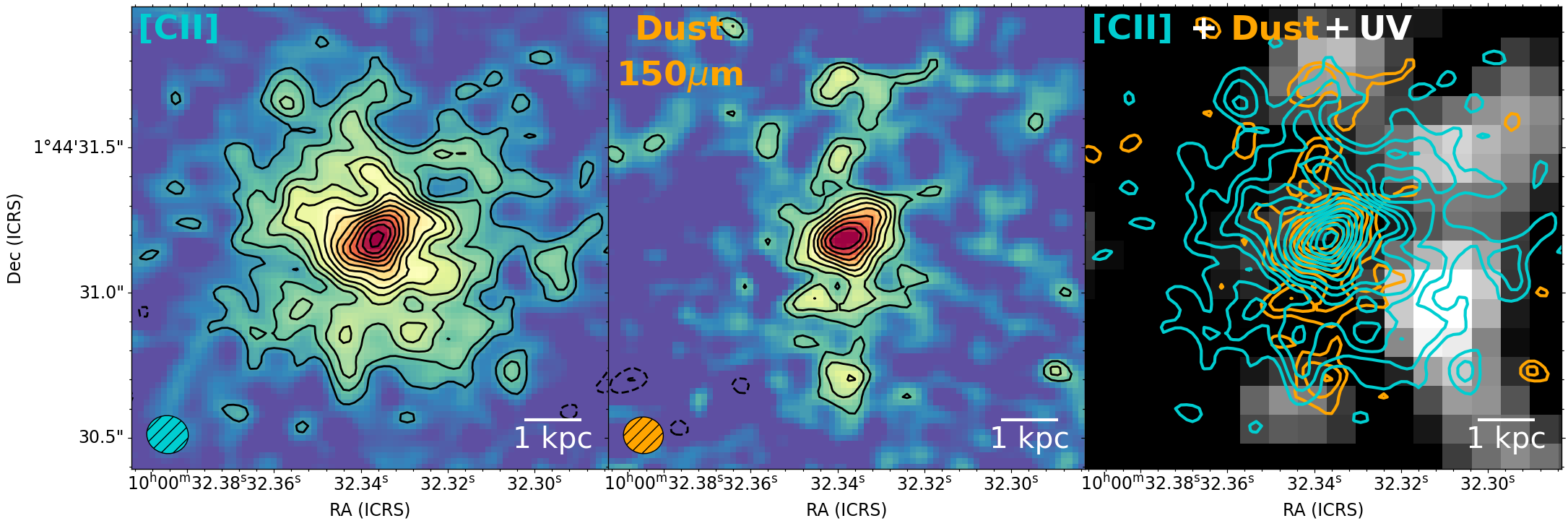
Left: [CII] moment-0 map of REBELS-25 at 0.13 arcsec resolution (~700 pc), with contours showing 2, 3, ...14 sigma emission. Centre: Dust continuum map, with orange contours showing 2, 3, ...10 sigma emission. Right: HST WFC3 F160W image from the COSMOS-DASH mosaic with the [CII] emission and dust continuum shown by the turquoise and orange contours, respectively. Figure 1 fro (Rowland et al., 2024).

3DBAROLO kinematics fitting for REBELS-25. Emission is masked at 2 sigma. The first column on the left shows the observed data, the middle column the model and the column on the right shows the residuals. The first row is for the intensity map, the second row for the velocity field map and the bottom row for the velocity dispersion map. In all plots, the black cross and the ellipse mark the centre and the radial extent of the modelling, respectively. In the first two rows we also show the position angle of the best-fitting model by the dashed line. In the second row, the grey dots give an indication of the separation of each ring along the velocity field (0.11"). In the velocity field map of the data and model, we also plot the iso-contours from -180 to 180 km/s in 45 km/s increments. In all maps, the beam size is indicated by the turquoise ellipse in the bottom left corner.
References
2024
- REBELS-25: discovery of a dynamically cold disc galaxy at z = 7.31\mnras, Dec 2024